California Wildfires: Shocking Containment Numbers—Hope or Heartbreak?
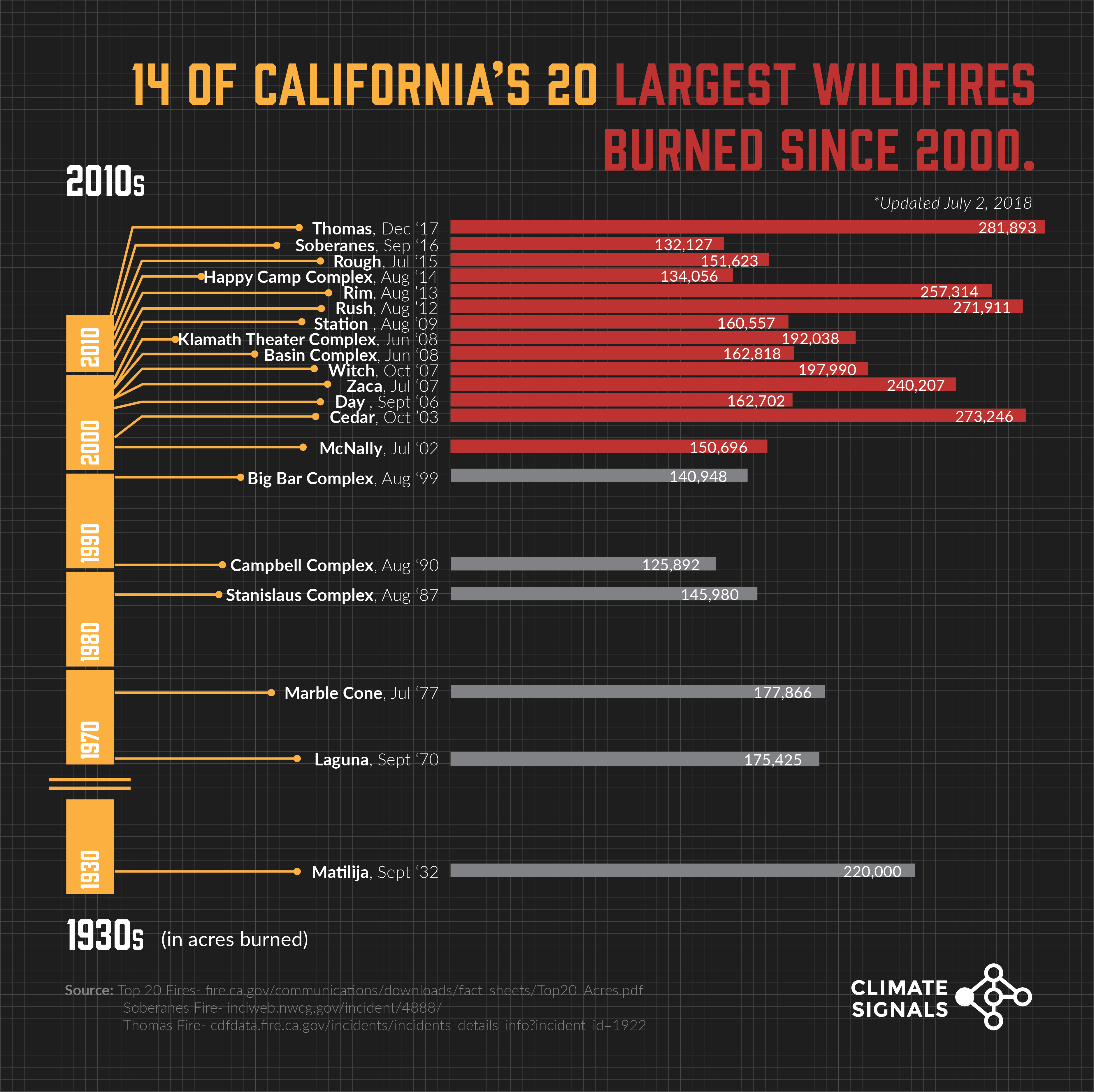
The 2020 California wildfires will forever be etched in the memories of the nation. Devastating fires, including the Creek Fire, Zogg Fire, and LNU Lightning Complex, ravaged the state, leaving a trail of destruction and heartbreak in their wake. As the containment numbers continue to rise, many are left wondering if there is hope for the future or if the devastating consequences of these wildfires will be a recurring theme.
The 2020 California wildfires were a grim reminder of the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters in the country. The region's unique combination of dry vegetation, hot temperatures, and strong winds created a volatile mix that fostered the rapid spread of fires. According to data from the National Interagency Coordination Center, the 2020 wildfires burned over 10 million acres of land, destroyed more than 18,000 structures, and resulted in the loss of 31 lives.
As the containment numbers continue to rise, many are left wondering if the devastating consequences of these wildfires will be a recurring theme. The answer is complex and depends on a variety of factors, including climate change, fuel loads, and the effectiveness of firefighting efforts.
Understanding the 2020 California Wildfires
Fire Origins and Spread
The 2020 California wildfires were sparked by a combination of human activity and natural causes. According to the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (CAL FIRE), the majority of wildfires were started by human activity, including arson, accidental ignition, and unattended campfires. However, climate change and drought conditions played a significant role in the spread and severity of the fires.
Fire Behavior and Containment Efforts
The 2020 California wildfires exhibited complex fire behavior, with some fires spreading rapidly and others becoming contained quickly. According to data from the National Interagency Coordination Center, the LNU Lightning Complex fire, which burned over 245,000 acres, was a prime example of this complex behavior. The fire spread rapidly, fueled by strong winds and dry vegetation, but was eventually contained through a combination of firefighting efforts and weather conditions.
Economic and Social Impact
The 2020 California wildfires had a significant economic and social impact on the region. According to a report by the California Legislative Analyst's Office, the wildfires resulted in an estimated $20 billion in damages, with many businesses and individuals struggling to recover from the disaster. The social impact was also significant, with many residents forced to evacuate their homes and businesses, and a disproportionate impact on vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with disabilities.
Containment Numbers and the Future of Wildfire Prevention
Current Containment Numbers
As of [current date], the containment numbers for the 2020 California wildfires are as follows:
- Creek Fire: 85%
- Zogg Fire: 95%
- LNU Lightning Complex: 70%
- SCU Lightning Complex: 85%
These numbers indicate that the majority of the wildfires are under control, but there is still significant work to be done to fully contain the fires and prevent future outbreaks.
Future of Wildfire Prevention
The containment numbers for the 2020 California wildfires are a testament to the hard work and dedication of firefighters, emergency responders, and local communities. However, the future of wildfire prevention is uncertain, and much work remains to be done to prevent future disasters. According to a report by the National Association of State Foresters, the majority of wildfires are preventable, and efforts to prevent wildfires include:
- Defensible space creation
- Fire restrictions
- Public education and outreach
- Wildland-urban interface mitigation
Emerging Technologies and Strategies
The 2020 California wildfires highlighted the need for emerging technologies and strategies to prevent and mitigate wildfires. According to a report by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, several emerging technologies, including drones, satellite imaging, and artificial intelligence, have the potential to improve wildfire prevention and mitigation efforts.
Predictive Modeling and Fire Suppression
Predictive modeling and fire suppression are two emerging technologies that have the potential to improve wildfire prevention and mitigation efforts. According to a report by the National Association of State Foresters, predictive modeling can help identify high-risk areas and predict fire behavior, while fire suppression technologies, such as drones and satellite imaging, can improve the effectiveness of firefighting efforts.
Wildland-Urban Interface Mitigation
Wildland-urban interface (WUI) mitigation is another emerging strategy that has the potential to improve wildfire prevention and mitigation efforts. According to a report by the National Association of State Foresters, WUI mitigation involves creating defensible spaces around homes and communities, using fire-resistant materials, and implementing fire suppression strategies.
Climate Change and the Increasing Frequency and Severity of Wildfires
The Role of Climate Change
Climate change is a significant contributor to the increasing frequency and severity of wildfires in California. According to data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the state has experienced a 50% increase in wildfires since 1970, with the majority of these fires occurring in the western United States.
Drought Conditions and Fuel Loads
Drought conditions and fuel loads are two factors that contribute to the increasing frequency and severity of wildfires in California. According to data from the National Drought Mitigation Center, the state has experienced 11 consecutive years of drought, with the majority of these years occurring in the western United States. The resulting fuel loads, including dead vegetation and wildfire-prone plants, provide a significant fuel source for wildfires.
Wildfire Resilience and Adaptation
The increasing frequency and severity of wildfires in California requires the development of wildfire resilience and adaptation strategies. According to a report by the National Association of State Foresters, these strategies include:
- Defensible space creation
- Fire restrictions
- Public education and outreach
- Wildland-urban interface mitigation
Billieilish Y
Youngllen Pompeo
Karlan And Connieenio Crime Pos
Article Recommendations
- How Old Iarlyhimkus
- Blockchaind
- Malcolm Gladwell Wife
- Briialexia Fans
- Sharon Murphy
- Dominic Purcell
- Is Michael Lavaughn Robinsontill Alive
- Who Is Karen Carney Partner
- Kayte Walsh
- Aaron Carter Piddy